SNCR Technology
What is SNCR?
 SNCR is an abbreviation for Selective Non Catalytic Reduction.
SNCR is an abbreviation for Selective Non Catalytic Reduction.
By dosing the right amount of reducing agent at the right temperature, between 850-1050°C, in e.g. an incineration plant, you can reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by between 50-80%. In tests, reductions of over 90% have also been noted.
The reduction takes place as follows, with ammonia.
4 NO + 4 NH3 + O2 → 4 N2 + 6 H2O
The alternative to ammonia is urea, which reacts to ammonia before reduction can take place as follows. NH2CONH2 + H2O → 2 NH3 + CO2
NOx-SOL’s SNCR system can use both reducing agents.
The alternative to SNCR to reduce NOx is SCR. Then you have a catalyst to reduce NOx. There is usually a factor of 15 – 20 difference in price, as SCR is more expensive than SNCR. SCR has a higher efficiency of the added reducing agent. The reason for the introduction of requirements for NOx reduction is that NOx is acidifying, eutrophic and irritates the respiratory tract.
Together with sunlight and organic compounds, it contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone.
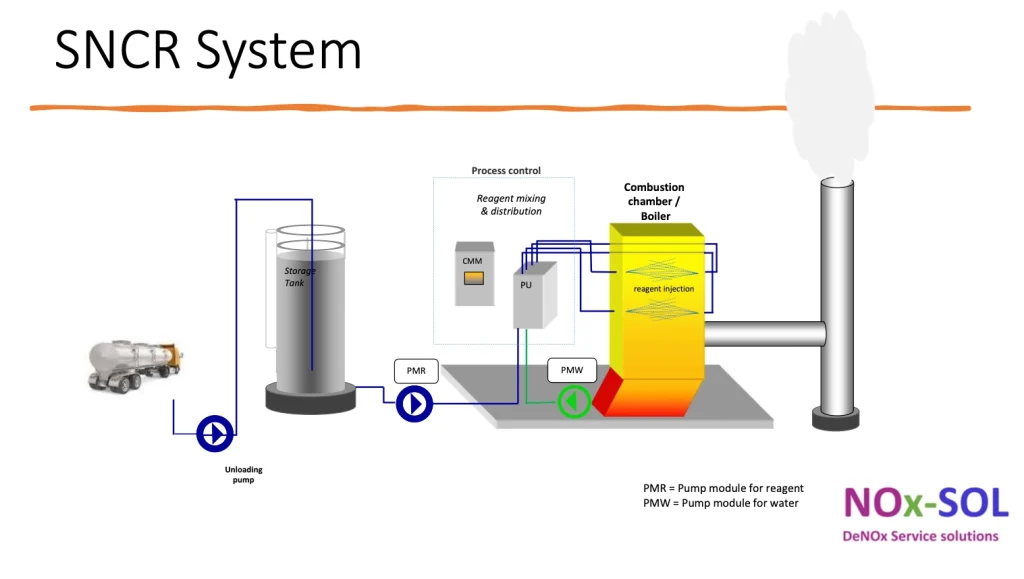
NOx-SOL's SNCR-system
The new SNCR system we are delivering today is a further development of the system that Petro Miljö previously delivered. In our system, we have upgraded the program and mixing module with new components and more control valves. This allows us to control the amount of reducing agent precisely to each individual injection point at the right time, as the temperature window or flue gas flow changes.
An SNCR system can be divided into the following main components:




